What are the three types of bearings?
Bearings are critical components in all rotating equipment, bearing the rotational function and corresponding loads. The design, structure, and performance of bearings directly determine the stability, efficiency, lifespan, and safety of equipment operation. Whether it's a lightweight automated device or a marine engineering vessel weighing thousands of tons, every piece of equipment relies on suitable bearing types to achieve efficient operation.
Among the many classification methods, the three most widely recognized basic bearing types in the industry are: Ball Bearings, Roller Bearings, and Precision Bearings.
These types are not only core components of traditional mechanical equipment but also the foundation for the continuous upgrading of future high-end equipment technologies. This article will systematically analyze the importance of these three types of bearings from an engineering perspective, how to select them, and, through LTZC's manufacturing and application experience, build a professional and reliable bearing knowledge system for readers.
1.What are the characteristics of the three bearing types?
Spherical rolling elements → Compact structure, flexible rotation, suitable for high speeds
Roller-shaped rolling elements → Large contact area, high load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy loads
High-precision structure and strict tolerances → Corresponding to precision bearings, used in high-performance equipment.
| Operating Factor | Determination |
|---|---|
| Load type (radial / axial / tilting moment) | Determines whether a ball structure or roller structure is used |
| Rotational speed & temperature rise | Affects lubrication, material selection, and geometric precision |
| Available installation space (bearing size) | Influences structural configuration and rolling element size |
| Precision requirements | Determines whether a precision bearing is needed |
| Environmental conditions (temperature, corrosion, dust) | Determines sealing type, material selection, and surface coating |
2.What is a Ball Bearing?
Ball bearings are the most widely used type of bearing in industrial applications. They reduce friction through point contact, with common types including four-point contact ball bearings and double-row roller bearings, enabling them to achieve high speeds, low noise, and low heat generation.
2.1 Ball bearings have the following advantages:
Low starting torque and smooth rotation
Maintain stable temperature rise in high-speed environments
Low requirements for lubricant viscosity
Can withstand moderate radial and limited axial loads
Wide range of bearing sizes, suitable for everything from small instruments to large machinery
2.2 Ball bearings have the following limitations:
Small point contact bearing area, unsuitable for ultra-heavy loads
Lower impact resistance than roller bearings
Sensitive to raceway geometry accuracy
2.3 LTZC Ball Bearings
LTZC has advanced ball bearing technology to the field of large equipment, producing various double-row ball slewing bearings through structural reinforcement and raceway optimization.
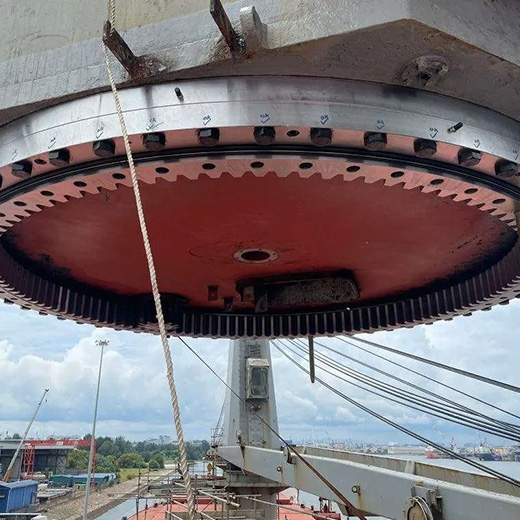
Its typical features include: high anti-overturning moment; suitable for wind turbine yaw, crane loading platforms, and engineering rotating devices; bearing size from 500mm to 6000mm or even larger; these products require extremely high raceway coaxiality control, which is also an important advantage of LTZC in the large ball slewing bearing market.
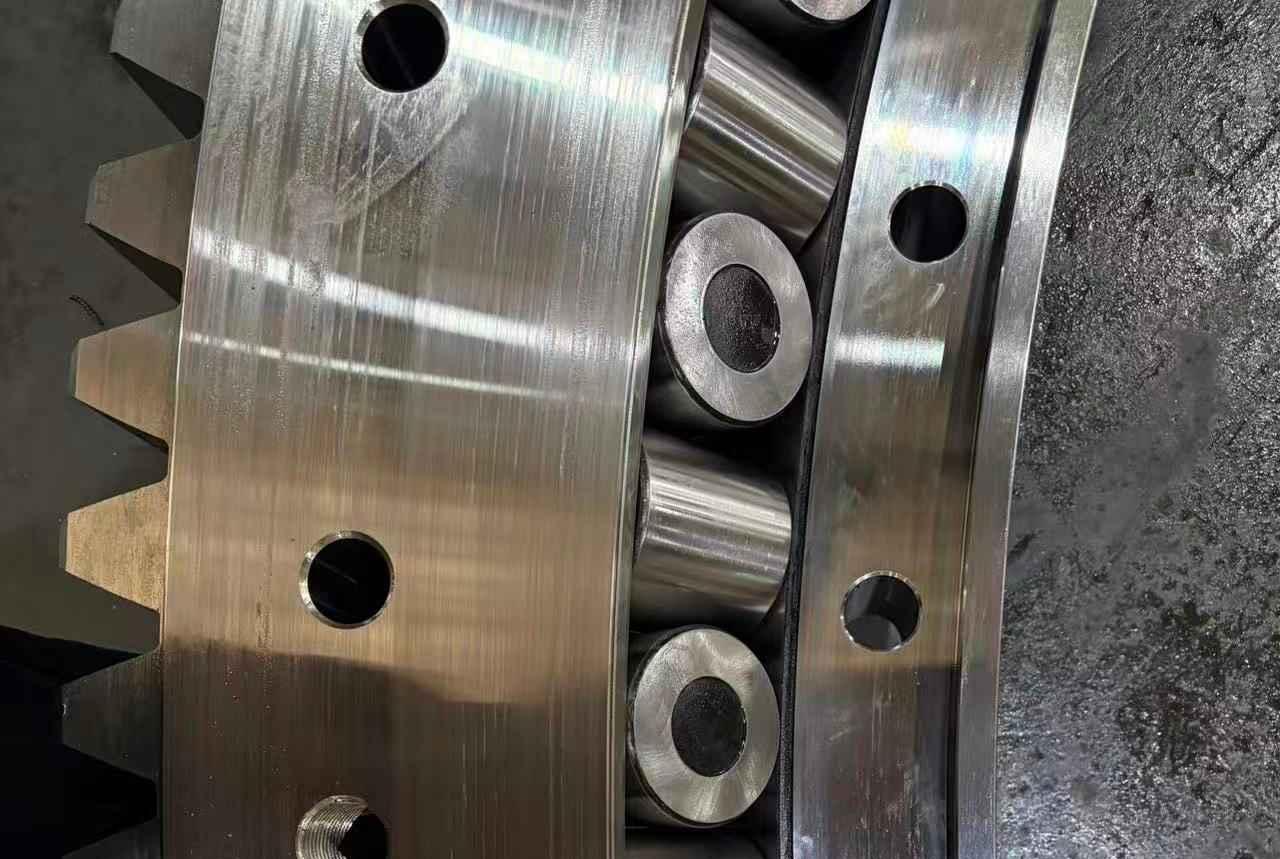
3. What Makes a Roller Bearing Different?
Roller bearings are a type of bearing designed for "high load and high stiffness." The line contact between the rollers and raceways allows them to distribute pressure, improving load-bearing capacity while reducing rolling element deformation.
3.1 Why Do Roller Bearings Have Higher Load-Bearing Capacity?
Line contact means: a larger contact area, more uniform stress distribution on the rolling elements, and a much higher load-bearing capacity for the same dimensions compared to ball bearings.
Therefore, roller bearings are suitable for heavy loads, impact loads, and low to medium speed equipment, and are often used with high-viscosity grease or lubricating oil.
3.2 Key Roller Bearing Type: Cylindrical Roller Bearing
Cylindrical roller bearings are among the most frequently used roller bearings in industry due to their structural flexibility and performance stability.
Its main advantages include: high radial load capacity, availability of NU, NJ, NUP, NF and other structural types, and the ability to manufacture large bearing sizes, making it suitable for heavy equipment.
Learn more about LTZC bearings
Watch LTZC bearing video
| Type | Rib Structure Characteristics | Axial Load / Displacement Capacity | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| NU-type cylindrical roller bearing | Outer ring with double-side ribs; inner ring without ribs | Allows bidirectional axial displacement; withstands radial loads only | Automotive gearboxes, conveyor rollers, motor spindles |
| NJ-type cylindrical roller bearing | Outer ring with double-side ribs; inner ring with one fixed rib | Handles unidirectional axial loads; restricts axial movement in one direction | Mining equipment, agricultural machinery, vibrating screens |
| NUP-type cylindrical roller bearing | Outer ring with double-side ribs; inner ring with one fixed rib + one detachable flat rib | Handles bidirectional axial loads; restricts bidirectional axial displacement | Gearboxes, marine propulsion systems, machine tool spindles |
| NF-type cylindrical roller bearing | Inner ring with double-side ribs; outer ring with one rib | Handles unidirectional axial loads; restricts axial movement in one direction | Machine tools, robotics systems, precision industrial instruments |
3.3 Why Choose LTZC Roller Bearings?
High-purity forgings
Multi-stage heat treatment and deep hardening process
High-precision raceway grinding and ultra-precision machining
Capable of stably producing large-diameter roller bearings ranging from several meters to tens of meters, with bearing sizes covering 300mm-15000mm
This enables LTZC to serve long-term applications in extreme working conditions such as tunnel boring machine main bearings, offshore lifting equipment, and large wind power structures.
Get LTZC bearing quote

4. Why Does Bearing Size Influence Performance and Reliability?
4.1 Direct Impact of Bearing Size on Performance
**Load Capacity:** The larger the outer diameter and the larger the rollers or balls, the stronger the load capacity.
**Speed Capacity:** Smaller bearing sizes are more suitable for high speeds.
**Stiffness:** Large bearings are typically used in high overturning moment scenarios.
**Thermal Stability:** Larger sizes involve more complex heat transfer and temperature rise management.
**Installation Requirements:** Large bearings have extremely high requirements for structural support and coaxiality.
4.2 Common Misconceptions in Bearing Selection
**Choosing an oversized bearing:** High cost, increased resistance, wasted structural space
**Choosing an undersized bearing:** Insufficient lifespan, inadequate load capacity, structural risks
**Ignoring actual load impact:** Service life far below design lifespan
In engineering practice, bearing selection involves steps such as lifespan calculation, material coefficients, lubrication strategies, and load spectrum analysis, thus requiring support from professional manufacturers.
Get LTZC bearing quote
4.3 LTZC's Professional Engineering Services
Life and Load Calculations
Bearing Type Structural Optimization Recommendations
Bearing Sealing and Lubrication Solutions
Early Wear Analysis
Bearing Size Custom Design
Bearing Installation and Maintenance Guidance
These services help users reduce maintenance costs and improve the long-term reliability of their equipment.
Get LTZC technology support
5. What Makes LTZC a Trusted Bearing Partner?
(1) 20 years R&DExpertise:
LTZC boasts over thirty years of professional experience in the manufacturing of large-diameter bearings, heavy-duty slewing bearings, precision bearings, and roller bearings. Leveraging its proprietary R&D and materials technology, LTZC's products not only meet international standards but also withstand extreme operating conditions.
(2) Extensive Engineering Application Experience:
LTZC's products are widely used in wind power, marine engineering, port machinery, tunnel boring machines, robotics, and aerospace, possessing a wealth of operational data that enables LTZC to provide clients with professional advice based on practical applications.
(3) International Certification Guarantees Authority
Certified by ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001 and multiple classification society certifications (ABS, BV, CCS), and possessing a complete testing system, including: coordinate measuring machine, gear precision testing, and life testing equipment.
(4) High Reliability and Stable Delivery Capability
LTZC's independent manufacturing system (forging—heat treatment—precision grinding—assembly—inspection) enables it to maintain a leading edge in quality, delivery time, and cost control, and provides customers with continuous and stable supply guarantees.