How to select slewing bearing?
How to select a Slewing Bearing?
Choosing a slewing bearing is not a simple purchase decision, but an engineering process that determines the reliability, precision, efficiency, and long-term safety of the entire machine. Whether the application is heavy-duty construction machinery, offshore systems, industrial automation, wind power generation, or aerospace-grade precision equipment, the correct selection of the slewing bearing determines the stability and safety of the system throughout its entire lifecycle.
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting a Bearing?
Slewing bearings are designed to withstand combined loads—axial moment, radial moment, and overturning moment—and are typically designed to operate under harsh environmental conditions.
Understanding Load Conditions
The most fundamental step is determining how the equipment transmits forces to the slewing bearing. LTZC engineers typically begin with the following three main load categories:
Vertical axial loads generated by lifting forces, structural weight, or downward forces.
Radial loads generated by horizontal forces, offset loads, or rotational inertia.
Overturning moment refers to the overturning torque caused by eccentric loads or dynamic overturning.
Most applications combine these three forces to varying degrees, thus requiring slewing bearings to safely withstand peak forces and ensure stable load-bearing capacity. LTZC's engineering team performs load simulations and safety factor optimizations to ensure the appropriateness of raceway geometry and rolling element selection.
Speed and Duty Cycle
Speed is often overlooked in bearing selection, but it significantly impacts bearing lubrication strategies, seal design, cage materials, and overall bearing structure. Low-speed and intermittent rotation allows for the use of extra-heavy bearing types, such as three-row roller bearings. Continuous or semi-continuous rotation requires tighter tolerance control, optimized lubrication flow, and better heat dissipation.
LTZC's CNC turning, raceway grinding, and precision measurement systems enable the production of bearings suitable for low-speed heavy machinery and high-precision industrial automation platforms.
Operating Environment
Slewing bearings typically operate in harsh environments: such as offshore platforms exposed to salt spray, excavators exposed to silt, and wind turbines experiencing extreme temperature variations. LTZC assesses complex environmental conditions, including corrosion exposure, humidity levels, abrasive particles, vibration intensity, chemical contact, and anticipated shocks. These environmental conditions not only affect bearing type but also sealing materials, corrosion-resistant coatings, and lubrication cycles.
Installation Space and Structural Constraints
Due to space constraints in bearing installation, the bearing's outer diameter, inner diameter, gear module, bolt circumference, and pitch must be considered to ensure ease of installation and maintenance.
LTZC specializes in manufacturing slewing bearing, non-standard bearing, precision bearing, thin-section bearing, heavy-duty bearing, and custom bearings, enabling perfect integration of customers' machinery with their bearing structures.
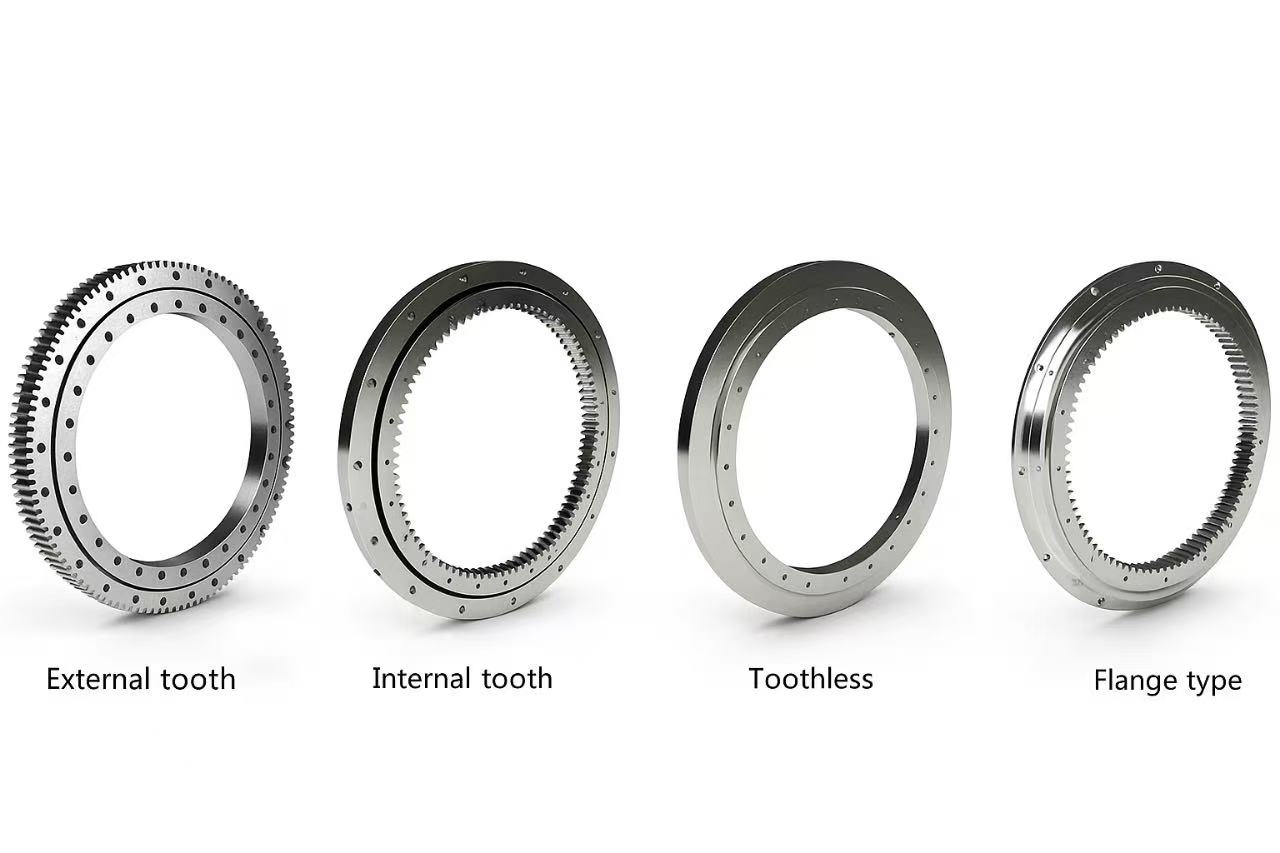
What types of slewing bearings are available?
Understanding the available bearing types is a key step in selecting the right solution. Slewing bearings vary significantly in load capacity, stiffness, precision, and cost.LTZC produces four main global slewing bearing series, each tailored to specific engineering needs.
Four-Point Contact Ball Slewing Bearing – Versatile Performance
Due to its flexibility and compact design, the four-point contact ball slewing bearing is one of the most widely used types of slewing bearings.
Key Features
Can withstand combined axial, radial, and moment loads
Simple design, lightweight bearing
Suitable for medium-load applications, enabling efficient load distribution
Applications:Widely used in truck cranes, rotating platforms, aerial work platforms, packaging machinery, and light industrial turntables.
Double-Row Roller Slewing Bearing – Enhanced Support and Stability
Two rows of balls, enabling independent load paths
Higher axial and radial load capacity compared to single-row designs
Applications:Tower cranes, construction hoists, industrial lifting equipment, heavy material handling platforms.
Crossed Roller Slewing Bearing – High Precision, High Rigidity
Can withstand extremely high overturning moments
High rotational accuracy
Orthogonally arranged cylindrical rollers
Applications: Robotic arms, aerospace turntables, radar systems, medical imaging equipment, semiconductor equipment
Three-Row Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing – Maximum Load Capacity
Three rows of rollers for even load distribution
Durable and long lifespan
Primarily used in heavy equipment, large excavators, offshore cranes, ship deck cranes, wind turbines, mining machinery, steel mills

Why is bearing selection so crucial?
Many failures are not caused by the bearing itself, but by improper selection, installation, or lubrication. LTZC's engineering team provides: Load analysis, Customized bearing CAD models, Gear selection recommendations, Bearing lubrication plan planning, and Bearing installation and maintenance guidance.
How to confidently choose the best slewing bearing?
Choosing a slewing bearing is an engineering decision that requires careful analysis of the equipment's operating environment, bearing load capacity, bearing type and structure, and the support of a reputable manufacturer. LTZC's integrated production system, advanced processing technology, and over 30 years of bearing R&D experience ensure that every bearing delivers high performance and long service life.
In summary:
Comprehensively evaluate bearing load, speed, and environmental conditions.
Understand the advantages of different bearing types.
Choose a reliable bearing manufacturer with complete process capabilities.
Validate bearing lubrication and sealing strategies.
Follow precise installation and maintenance guidelines.
Get professional support by collaborating with LTZC's engineering team.
Still haven't resolved your project issue? Get LTZC technical support now!